vpnpitbull.com – which statement is true about blockchain. Curious about blockchain technology? This article dives deep into answering the question, “Which statement is true about blockchain?” Explore the facts, debunk the myths, and gain a comprehensive understanding of this revolutionary technology.
Blockchain, the backbone of Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has emerged as a transformative technology with immense potential. Yet, it remains a topic of confusion and intrigue for many. If you’ve ever wondered, “Which statement is true about blockchain?”
you’re not alone. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the truths and dispel the misconceptions surrounding blockchain. Whether you are a tech enthusiast, an entrepreneur, or a curious individual, let’s venture into the world of blockchain to understand its implications and untangle the web of myths and facts.
Which Statement is True About Blockchain?
What is Blockchain?
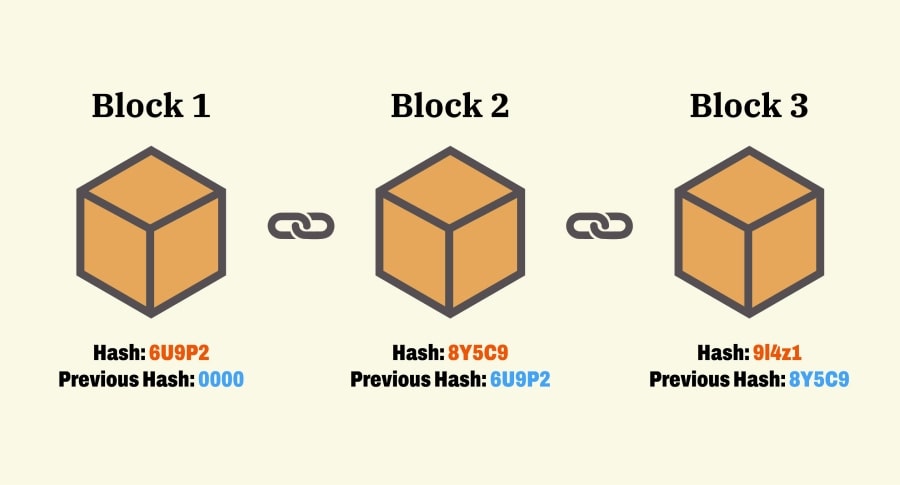
Before we delve into the true statements about blockchain, let’s grasp the fundamental concept. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology. It allows for secure and transparent recording of transactions across a network of computers, known as nodes. Each transaction, or “block,” is linked to the previous one using cryptographic techniques, forming an immutable chain of blocks. This design ensures that the data stored on the blockchain cannot be altered or tampered with easily.
Blockchain, often referred to as the “distributed ledger technology,” is a revolutionary system designed to record and verify transactions in a secure, transparent, and decentralized manner. It serves as the foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its potential applications extend far beyond the realm of digital currencies. Understanding the intricacies of blockchain is crucial in unraveling the true statements about this transformative technology.
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary system of recording and verifying transactions in a secure, transparent, and decentralized manner. It is the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its applications extend beyond digital currencies. At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger that enables the secure and tamper-proof storage of data across a network of computers.
Key Characteristics of Blockchain Technology:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems that rely on a single authority or intermediary, blockchain operates on a network of computers known as nodes. Each node holds a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring that no single entity has full control over the data or the network.
- Immutable Ledger: Transactions recorded on the blockchain are grouped into blocks, and each block is linked to the previous one using cryptographic techniques, creating a chain of blocks. Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or delete the data within it. This immutability ensures data integrity and transparency.
- Consensus Mechanism: To add a new block to the blockchain, the majority of nodes in the network must agree on its validity. Different consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS), are used to achieve agreement among the nodes.
- Transparency: All transactions on the blockchain are open and visible to all participants in the network. This transparency ensures accountability and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation.
- Security: Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic algorithms to secure data and prevent unauthorized access. The decentralized nature of the network and the consensus mechanisms add an additional layer of security, making it resistant to hacking and tampering.
How Blockchain Works:
- Transaction: When a transaction occurs, it is broadcast to the network and grouped with other transactions to form a block.
- Verification: Nodes in the network compete to validate the transactions in the block using the consensus mechanism. Once validated, the block is added to the blockchain.
- Consensus: Consensus mechanisms ensure that all nodes agree on the validity of the transactions. In PoW, miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to compete for the right to add a block, while in PoS, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
- Decentralization: As each node maintains a copy of the blockchain, there is no central point of control, making the system more resilient and less prone to single points of failure.
Applications of Blockchain Technology:
- Cryptocurrencies: The most famous application of blockchain technology is in the creation and operation of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain enables the creation of self-executing smart contracts, which automatically execute predefined conditions when met, eliminating the need for intermediaries in various agreements and transactions.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track and verify the movement of goods and products in a transparent and tamper-proof manner, enhancing supply chain efficiency and transparency.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain offers a secure and transparent way to conduct elections, ensuring the integrity of the voting process and preventing voter fraud.
- Identity Management: Blockchain can provide a secure and decentralized system for managing digital identities, giving individuals control over their personal data.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Understanding the inner workings of blockchain is essential to identify the true statements about it. Here’s a simplified step-by-step explanation:
- Data Structure: Each block contains transactional data, a timestamp, and a unique cryptographic hash.
- Consensus Mechanism: To add a new block to the chain, the majority of nodes in the network must agree on its validity. This consensus mechanism varies, with Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) being the most common.
- Immutability: Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or delete the data, ensuring transparency and security.
Public vs. Private Blockchain
Blockchain technology has gained significant attention for its potential to transform various industries. When exploring blockchain networks, one encounters two primary types: public and private blockchains. Understanding the differences between these two variations is essential in deciphering which statement is true about blockchain and how it can be effectively utilized in different scenarios.
What is a Public Blockchain?
Public blockchains, also known as open or permissionless blockchains, are networks where anyone can participate, validate transactions, and become a node. These networks are truly decentralized, relying on a large number of nodes scattered globally to reach consensus and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
Key Characteristics of Public Blockchains
- Open Participation: Anyone can join the network, verify transactions, and contribute to the consensus process. There are no restrictions on who can become a part of the network.
- Transparency: All transactions on the public blockchain are visible and accessible to anyone. This high level of transparency ensures accountability and prevents hidden manipulation of data.
- Security: Public blockchains are secured through cryptographic algorithms and economic incentives. The Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, used by networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum, ensures that malicious actors would need an impractical amount of computational power to tamper with the blockchain.
- Incentives: Participants in public blockchains are incentivized to behave honestly through the issuance of cryptocurrency rewards. For example, Bitcoin miners receive newly minted Bitcoins and transaction fees for validating blocks.
Use Cases of Public Blockchains
- Cryptocurrencies: The most famous application of public blockchains is for digital currencies, such as Bitcoin and Litecoin, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Public blockchains are the backbone of DeFi platforms, providing open and accessible financial services, including lending, borrowing, and trading.
- Transparent Supply Chains: Public blockchains can be employed to track and verify the origin and authenticity of products, promoting transparency in supply chain management.
- Tokenization of Assets: Public blockchains facilitate the tokenization of real-world assets, enabling fractional ownership and enhancing liquidity in traditionally illiquid markets.
Keep Reading : ProxiGuard Secure Video Streaming with Croxy for Unlimited
Private Blockchain: Control and Privacy
What is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains, also known as permissioned blockchains, are networks with restricted access and participation. In a private blockchain, the entity managing the network controls who can become a participant and access the data.
Key Characteristics of Private Blockchains
- Limited Access: Participation in a private blockchain is controlled by a centralized entity. Participants are usually known entities with permission to access the network.
- Privacy: Private blockchains often offer higher levels of privacy compared to public blockchains. Transactions and data visibility may be restricted to specific participants.
- Centralization: Although blockchain technology is still utilized, private blockchains tend to be more centralized compared to their public counterparts. The management and decision-making authority often rest with a single organization or consortium.
- Faster Transactions: Private blockchains generally have faster transaction processing times since they involve a smaller number of nodes, and consensus may be achieved more quickly.
Use Cases of Private Blockchains
- Enterprise Applications: Private blockchains are commonly adopted by businesses and enterprises for internal processes like supply chain management, inventory tracking, and record-keeping.
- Consortium Networks: Consortia of companies or organizations with shared interests may use private blockchains to collaborate on projects or share sensitive data securely.
- Identity Management: Private blockchains can be employed for identity verification and management, ensuring secure access to sensitive information.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industries with specific regulatory requirements, such as healthcare and finance, may use private blockchains to maintain compliance while leveraging the benefits of blockchain technology.
Keep Reading : How to Disable VPN on iPhone Mode
Public vs. Private Blockchain: Making the Choice
The decision between public and private blockchains depends on the specific requirements of the use case and the desired level of decentralization, transparency, and control. Public blockchains offer unparalleled transparency and decentralization but may not be suitable for scenarios requiring privacy and restricted access. On the other hand, private blockchains provide more control and privacy but might sacrifice some of the advantages associated with decentralized networks.
Blockchain Limitations
Blockchain technology has undoubtedly shown immense promise and potential in revolutionizing various industries. However, like any emerging technology, it comes with its own set of limitations and challenges. Understanding these limitations is essential to gain a balanced perspective on blockchain’s capabilities and to identify areas that require further research and development.
Keep Reading : Do VPN Still Works when Using Incognito Mode?
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has come a long way since its inception, and its future holds exciting possibilities. As the world becomes increasingly digital and interconnected, blockchain is poised to play a pivotal role in reshaping industries, governance, and the way we interact with data. Here are some key trends and potential developments that indicate a promising future for blockchain:
Scalability Improvements
Scalability has been a primary concern for blockchain networks, particularly public ones. As the demand for faster transaction processing and higher throughput increases, developers are actively working on scalability solutions. Technologies like sharding, layer-two protocols (such as Lightning Network for Bitcoin), and advancements in consensus mechanisms are poised to significantly improve the scalability of blockchain networks. These improvements will enable blockchain to handle a higher volume of transactions and compete with traditional payment systems.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
The energy-intensive nature of some blockchain consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work, has been a subject of criticism. To address environmental concerns, the industry is transitioning towards more energy-efficient alternatives like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and other consensus models. PoS requires significantly less computational power, making it a greener option. Additionally, innovations in renewable energy and the integration of blockchain with sustainable initiatives are likely to further enhance the technology’s sustainability and reduce its ecological footprint.
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions
The future of blockchain lies in achieving interoperability between different blockchain networks. Efforts are underway to develop cross-chain solutions that facilitate seamless data exchange and transactions between disparate blockchains. Interoperability will enable enhanced collaboration, data sharing, and the development of decentralized applications that leverage the strengths of multiple blockchains. This will lead to a more interconnected and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
Hybrid and Federated Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains, combining features of both public and private blockchains, are emerging as a promising solution for various use cases. They offer the benefits of public blockchains in terms of transparency and decentralization, while also providing the privacy and control associated with private blockchains. Federated blockchains, where specific nodes or entities have more authority in the consensus process, can enhance scalability and efficiency while maintaining some level of decentralization.
Blockchain in IoT and Supply Chain
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, blockchain’s tamper-proof nature and secure data sharing capabilities make it an ideal match for IoT applications. Blockchain can provide a trust layer for IoT devices, enabling secure communication, data integrity, and autonomous machine-to-machine transactions. Additionally, supply chain management is likely to witness significant disruption as blockchain technology ensures transparency and traceability, reducing fraud and increasing consumer confidence.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central banks around the world are actively exploring the concept of issuing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). CBDCs are digital versions of a country’s fiat currency, built on blockchain technology. They offer potential benefits such as faster and more cost-effective cross-border transactions, financial inclusion, and improved monetary policy implementation. The widespread adoption of CBDCs could revolutionize the global financial landscape.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Expansion
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has gained significant traction, offering a range of financial services without intermediaries. The DeFi ecosystem is likely to continue growing, providing more diverse investment opportunities, lending, borrowing, and insurance services. As DeFi platforms mature and address security concerns, they could become mainstream alternatives to traditional financial institutions.
Regulation and Standards
Blockchain technology’s future will also depend on the establishment of clear and supportive regulations. Governments and regulatory bodies are gradually recognizing the potential benefits of blockchain while aiming to protect consumers and maintain financial stability. The creation of standardized frameworks for blockchain applications and digital assets will foster innovation and wider adoption.
Keep Reading : Avoid a Crypto Pump and Dump
FAQ about Blockchain Technology
Q : What is blockchain technology?
A : Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that securely records and verifies transactions across a network of computers. It operates on cryptographic principles, ensuring transparency, immutability, and resistance to tampering.
Q : What are the types of blockchain?
A : There are primarily two types of blockchain – public and private. Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open and permissionless, allowing anyone to participate. Private blockchains restrict access and participation to known entities, offering more privacy and control.
Q : What are the limitations of blockchain technology?
A : Some limitations of blockchain include scalability challenges, energy consumption (in certain consensus mechanisms), lack of regulation and standards, security concerns in smart contracts, and the difficulty of altering recorded data due to blockchain’s immutability.
Q : What is the future of blockchain technology?
A : The future of blockchain looks promising, with ongoing efforts to improve scalability, energy efficiency, and interoperability. Blockchain is expected to find applications in various industries, revolutionizing finance, supply chain management, voting systems, and identity management.
Q : Is it true that a blockchain carries no transaction cost? True/False?
A : False. While some blockchains may have lower transaction costs compared to traditional systems, there are still transaction fees associated with validating and adding transactions to the blockchain.
Q : How does blockchain encourage trust among peers?
A : Blockchain fosters trust among peers through its decentralized and transparent nature. All transactions are visible and verified by consensus, ensuring that no single entity has control over the data. The immutability of the blockchain further strengthens trust by preventing data tampering.
Q : Which one of the following describes a blockchain?
A : A blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that securely records and verifies transactions across a network of computers.
Q : Which of the following is important for blockchain?
A : Transparency, decentralization, security, immutability, and consensus mechanisms are all important aspects of blockchain technology.
Conclusion
Blockchain, at its core, is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that has emerged as the foundation of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. However, its potential extends far beyond digital currencies. It offers transparency, security, and immutability, making it suitable for various industries, from supply chain management to healthcare and finance.
True statements about blockchain include its inherent security, achieved through cryptographic techniques and decentralized consensus mechanisms. Blockchain’s transparency ensures accountability and traceability, fostering trust in a world that increasingly relies on digital interactions.
While blockchain’s public perception might be synonymous with cryptocurrencies, it is essential to recognize its versatility and applications in domains such as voting systems, supply chain tracking, and identity management. Blockchain technology is a catalyst for decentralization, democratizing systems and minimizing the reliance on intermediaries.
However, like any emerging technology, blockchain has its limitations and challenges. Scalability, energy consumption, privacy concerns, and the need for standardized regulations remain focal points for development and research.
The future of blockchain holds tremendous promise. As the technology continues to evolve, scalability solutions, energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, interoperability, and innovative real-world applications will drive its widespread adoption. Hybrid models, combining the best features of public and private blockchains, will likely emerge, catering to diverse use cases and industry requirements.
As we venture further into the decentralized future, collaboration among governments, businesses, developers, and the wider community will be pivotal in shaping the full potential of blockchain. Embracing transparency, inclusivity, and sustainability, blockchain technology will lead us towards a world where trust is democratized, transactions are secure, and data integrity is assured.
In conclusion, understanding the true statements about blockchain empowers us to harness the potential of this groundbreaking technology. As it continues to transform industries and redefine how we interact in the digital age, blockchain holds the key to unlocking a future of transparency, security, and decentralization. Let us embrace this journey with curiosity, innovation, and responsible exploration, as we pave the way for a decentralized tomorrow.